
needs
spiral as a health basis for a healthy HUMAN
or
did Abraham maslow ever plot "Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Pyramid"?
A. G. Busigin, Professor, Doctor of Pedagogical Sciences
A. L. Busigina, Professor, Doctor of Pedagogical Sciences
Samara
State Pedagogical University
According to "State Report on the Russian Population's Health in 2002", "…the common sickness rate grew in 1992-2002 by 32,1%. The growth in sickness rate is observed in all illness categories" [3, p. 12]. This refers only to those people who applied for medical care to medical institutions.
The essential universal values in new spheres of human activities studied from the point of view of desmoecology[1] inevitably lead us to studying the interconnection of human needs and human health. Revealed are really astonishing and absurd things taking place for a number of years in scientific circles of professional psychologists, medical people, philosophers, educators, and sociologists.
There seems to be no "valid theory" of health yet. The issue of the "measure of a healthy human's health" has not been dealt with properly. Nobody tells people what to do so that not to fall ill and not allow the greedy "paid medicine" deceive you. Nobody tells people how to diagnose your health if you are not a doctor, a psychologist, or a sociologist, and what should be done to feel the delight of living on Earth up to the old age. Maslow's motivation doctrine which might be a basis for health theory, for setting goals and being satisfied with life has been distorted.
When studied carefully, the deepening ecological crisis insistently testifies to the global deterioration of health of the whole human population [1, p. 33]. People all over the world complain of strange illnesses ("big city melancholy", "workaholism", etc.), and of the universal crisis.
Let's first define the "health" notion. To ensure "translateability" of different sciences, any scientific notion has to be accurately determined, and its contents and structure have to be studied. In conditions of a global ecological crisis, when human health has taken an important place among universal values, the problem of human health and human population has involved a great number of various scientists – philosophers, teachers, psychologists, sociologists, natural scientists, engineers, and economists.
They all must be "armed" with properly developed and generally recognized terminology. That is why the "health" notion is fundamental here. At present, however, health is often interpreted in social, pedagogical, philosophic, and medical literature from different methodological and theoretical points of view.
By 1988 P.I. Kalyou [4] analyzed 79 definitions of human health formulated by representatives of different branches of science at different times and in different countries.
By the year 2000 the number of the definitions was more than 100: when
working out the definitions for this notion,
strikingly numerous interpretations were used by different scholars. No other category, even love, was paid so much attention to. And, it is understandable.
With increasing number of attempts to cope with the task, a
solution that could satisfy everyone has not been found yet. The most
popular, generally accepted and operative is the definition that was set forth
in the preamble to the World Health Organization Charter more than half a
century ago (in 1948). There the individual health was determined as "a
state of complete physical, spiritual, and
social well-being and not just absence of an illness or disability".
But even this definition was criticized by Professor G.S. Nikiforov for its weak practical orientation and
fuzziness [7, Page 43].
The
vast number of health definitions has made it necessary to classify them by 5
model groups:
1. "Medical health model. It implies a health definition that only contains medical symptoms and characteristics of health. Health is regarded as absence of illnesses and their symptoms.
2. Biomedical health model. Health is regarded here as absence of a physical disorder or a subjective sensation of ill health in an individual. The accent is made on natural and biological essence of man. Biological patterns of vital activities and health of a human being are emphasized as dominating.
3. Biosociological health model. The notion of health here includes both biological and social characteristics taken as a whole, with top priority given to the latter.
4. Social value health model.
Health is a value for a human being.
It is a prerequisite for a full-value life and satisfaction of man's material and spiritual needs (italicized in bold type by the writers), his or her participation in economic, scientific, cultural, and other activities.
The
definition formulated
by the World Health Organization [4]
fully corresponds to this model".
Please
note that the phrase italicized by the writers in the social value health model
testifies the priority of physical health. Therefore,
the social value health model which better corresponded to health definition
given by the World Health Organization and was adequate in the XX century is not the best, the
most comprehensive and universal in the XXI century:
in time of global ecological crisis the mental and social components of health
are not less important than the physical one.
There is another model, the so called "integrative model" discussed by E.A. Ovcharov [6] and based on the concept that "this notion should incorporate not one or two but a number of criteria. Some authors agree that the "health" notion should incorporate medical, biological, psychological, social, natural, functional, and environmental factors."
We
strongly object it. "Stuffed" with
numerous criteria taken from different areas of knowledge and reality, this
notion will be just a conglomerate but not a systematic unity. The
health notion enumerating "medical, biological, psychological, social,
natural, functional, and environmental factors" would be an awkward and difficult
to read treatise but not a definition. A definition must be like a "shot"
– a short, clear, purposeful, and systematically arranged phrasing.
Abraham
Maslow, a brilliant scholar, showed half a century ago (in 1954) that the
integrative[2]
and backbone notion "uniting" scientists of all trends are the basic
needs. It is amazing that psychologists, medical people, sociologists, and
economists who have been studying and teaching the motivation theory for 50
years (dozen generations of students!) "have not noticed" or
misunderstood an appeal for holism and integrative approach of the most
frequently quoted[3]
American psychologist of the Ukraine origin [5, pp.13-14].
In our opinion, the health definition should be based on integrative but not "multiple" factors. We suggest taking the basic needs system as an integrative factor which determines the whole life of any person. The basis for it was laid by A. Maslow in his theory:
1. "Based on the above, I state it flat and sharp that a person not satisfied with a basic need should be regarded as sick, or not completely human, at least.
2. Nothing will stop us to call sick those people who suffer from lack of vitamins or microelements. But who said that lack of love is less harmful to organism than lack of vitamins? Being aware of pathogenic effect of unshared love on organism, who will undertake to blame me for being unscientific just because I am trying to introduce such an "unscientific" problem as the value problem in the sphere of scientific discussion? Confronted with scurvy or pellagra, a physician discusses the role of vitamins. A psychologist has the same right to discuss values. Following this analogy, one may say that major driving force of a healthy human is a need of self-actualization. If a human is constantly influenced by some other need, he or she cannot be considered to be healthy. Such a human is ill, and it is as serious as salt or calcium imbalance [5, p.104].
3."We will never gain understanding of a human if we still ignore his or her highest aspirations. Such terms as "personality growth", "self-actualization", "striving for health", "search of identity and autonomy", "need of perfection" (and other terms denoting human aspirations "upwards") should be accepted and widely used as they describe common or maybe universal tendencies of humanity".
4. "I am trying to build a system of essential human values, a kind of a code of universal virtues that are good per se; they are naturally desired and therefore need not to be excused or stipulated.
5. This hierarchy of values is rooted in human nature.
6.A human does not just want or strive to achieve them, they are needed to him, needed to withstand illnesses and psychopathologies" [5, p. 17] (italicized in bold type by the writers).
The way out is to switch to noospheric health model [1, p. 61] in which all basic needs of every individual are equally[4] represented, with priority given to health of the whole present and future generations. The noospheric health model1 evolves from the danger of human race extinction followed by extinction of everything living on Earth, and as the aftermath, turning Earth into another dead planet.
To further develop the health notion, the issue of basic needs satisfaction measure has to be resolved. According to Maslow's theory, every human has several basic needs and lots of "secondary" ones of minor importance. If we further evolve the health notion articulated by the World Health Organization, then we may say that a human is "completely happy" when all his or her basic needs by Maslow's hierarchy are satisfied.
We suggest taking the basic needs "hyposatisfaction – hypersatisfaction" index as a measure of "complete happiness". This "hyposatisfaction - hypersatisfaction" is the cause of illnesses because human organism gets out of its normal state – out of balance[5]. Many people think that money cannot be too much but there are many rich people (many enough to speak of) who are stuck at this level of basic needs satisfaction and lost their aim in life and interest in strategic improvement of their personality. They withdraw into themselves, they see around only enemies who want to take away their property. They "stimulate" themselves with alcohol, drugs, etc. Their children are unhappy and unhealthy because having much money is not a qualitative measure of needs satisfied but a quantitative measure of satisfying one of them. Money cannot buy health, peace with oneself, love, or self-expression in sciences, arts, etc. Many of Olympic, world, and other champions become seriously ill, both physically and mentally, after they retired from sports.
Thus we regard the quantitative measure of needs satisfaction as follows: there is "necessity" (as in school books on Euclidean geometry) to satisfy needs, and there is "sufficiency" in satisfying them. Knowing the health definition, a person (from young years when practicing psychology and desmoecology [1, p. 138] at school or higher institution) must figure out the level he or she reached, assess personal health, and define a set of the most important needs which are better known to him or her than to anybody else[6]. It is impossible to "build" an exact "picture", and it will vary in the course of life, but this is a dialectical process.
We will have to use a mathematical form of putting down the health notion. Before choosing respective mathematical symbolism and notation, we would like to draw your attention to the following fact: the scientific world has been discussing how to interpret human health for a number of years. P. Kalyou emphasized the following principal point: health is defined as a state, as a dynamic process, or is completely ignored by different authors. He also noted that in earlier interpretations health was defined as a state. In the last decades the local and foreign scholars tend to consider health to be a dynamic process. There are some authors (e.g. Academician V. Kuznetsov) who do not even try to categorize the definition.
After a closer examination, the noospheric health model seems to imply medical, biomedical, biosociological, and social value health models[7]. It means health, taken in the broad sense of the word, is not only a prerequisite for satisfaction of material and spiritual needs but, in our opinion, is a state of organism (balanced state) in the process of satisfaction of all needs.
Summing up we may state that the noospheric health model implies the following: health is a triunuque dialectical notion, and is simultaneously (1) means of satisfaction, (2) process of satisfaction, and (3) result of equal satisfaction of physiological, psychological, and social needs of an individual.
Since the health definition must reflect one of the vital noospheric needs - a need of ensuring health maintenance for the present and future generations [1, p. 61], three noospheric (desmoecological) health definitions different in their completeness but equally valid for practical analysis of individual health can be formulated:
1."Individual Health of man is a means, process, and result of reaching equally balanced necessity and sufficiency in satisfaction of physiological, psychological, and social needs of an individual with priority given to maintenance of life and health of the whole present and future generations".
2."Individual health is a balance of necessity and sufficiency in satisfaction of physiological, psychological, and social needs of an individual with priority given to health of all generations of human population".
3."Health is a balance of necessity and sufficiency in satisfaction of basic needs".
The second point here is not only critical for defining health, but has immense gnoseological importance by itself. We have twice mentioned the term "basic needs spiral", while the whole scientific world have been using the notion of "Maslow's hierarchy of needs pyramid" for dozens of years. We state with full responsibility that this is a myth ascribed to the great psychologist of the XX century by those people who failed to understand him.
Maslow wrote in his book, "I cannot but mention an utterly distressing for me fact consisting in that this really revolutionary knowledge (a new concept of man, society, values, and new understanding of science, philosophy, etc.) has not caught eye of our intellectuals and is now and then deliberately ignored by them (italicized in bold type by the writers), especially by those who are in charge for communications with educated part of society and young people." [5, p.12]. It looks as if A. Maslow's hardships were not over in 1970 – the year when the second edition of his book was published and he, President of the American Psychological Association passed away. Afterwards, facilitated by some "easy" hand but not "holistic" head, "Maslow's hierarchy of needs pyramid" appeared in all textbooks on psychology. He surely became famous out of it, but we believe that it would not be to the great humanist's liking.
Not very thoughtful or analytically-minded readers were possibly misled by A. Maslow"s terms of "hierarchical structure" and " rigidity measure of the hierarchical structure".
Psychologically, "hierarchy" is always tied to "up going levels".
As a matter of fact, a ladder-type "pyramid"(actually a triangle in vertical plane) appeared as an image of human aspirations, divided into 5 or 7 levels – basic needs.
A legitimate question comes up: is it worth raising an alarm and does it matter whether Maslow meant a pyramid or not, once everybody got used to this historical fact?
What does the geometrical figure of pyramid denote and symbolize? (whatis it associated with in mass consciousness?)
The fact is that the most important up to now doctrine set forth on nearly 500 pages was shrunk to a one page[8] graphical representation, as shown in Fig.1.

Fig. 1. Maslow's hierarchy of needs pyramid. (1) physiological, (2) safety, (3) love and belongingness, (4) self-esteem, (5) self-actualization
There is nothing bad in it.
On the contrary, we are always for "shrinking" huge volumes of information [2, Fig.1] because it helps you avoid "being overflown" with information and develop integrative (holistic) thinking [2, p. 98] the mankind lacks in resolving such multi-factor problems as stable development strategy (to overcome global crisis[9]), or health.
The above graphical representation accounts for serious consequences: people do not bother to read those 500 pages, they only read extracts from Maslow's writing in textbooks and see there a triangle crossed with five to seven horizontal lines which completely cross the whole sense out of this revolutionary, breakthrough theory of everybody's life and behavior.
We were indignant with superficial treatment of Maslow's theory (the treatment foreseen by Maslow) and with the pyramid representation given by American psychologists K. Bayer and L. Scheinberg in their book that was not bad in general. This urged us to investigate the "pyramid issue". [9, p.23].
All people who studied geography, even children at school, associate a pyramid[10] with the Egyptian stone structures that have been standing unchanged for many thousand years and symbolize power of the fourth dynasty Pharaohs.
Against your will, your subconsciousness is being intuitively persuaded that the theory of needs and motivations does not represent dialectical laws of life and psychology which you cannot bypass but can only make practical use of for developing your personality [5, p.113], but is a stiff theoretical structure[11].
1. This may be supported by the following Maslow's ideas: "One should once and for all give up senseless attempts to list and catalogue human needs and wants" [5, p. 65].
2.
"The very catalogue structure and assigning some "inventory
numbers" to needs presupposes their mutual isolation, independence from
each other" [4,
p. 66]
. The pyramid gives an impression that "a human who feels a need cannot
feel another need at the same time. However, as stated above, interrelationships
among needs are not subject to the principle of mutual exclusion. On the
contrary, needs are so deeply intertwined that they are practically inseparable.
If we recollect that cognitive
capabilities (perceptive, intellectual, and learning capabilities) not
only help a human adapt but
also satisfy
his or her basic needs, then it becomes clear that inability to fulfill
these capabilities, any deprivation of them automatically poses a threat to
satisfaction of basic needs. Only accepting the above statement we can
get closer to understanding roots of human curiosity and inexhaustible striving
for knowledge and truth, his eagerness to solve the mystery of eternity and
being. Hiding the truth, censorship, lack of truthful information, and a ban on
communication threaten to satisfaction of all basic needs (pp.100,101,258 and
other].
3. "I am under the impression that modern motivation theories are based as a rule on false interpretation of motivation state as special, specific, detached from processes occurring on somatic and personal levels. Yet any motivation theory claiming to be persuasive must proceed from counter assumption. It must assume that motivation is continuous, infinite, and changeable being a universal characteristic of practically any organismic state" [5, p.95].
4. "After physiological and safety needs have been enough satisfied, the needs of love and belongingness become actual, and MOTIVATION SPIRAL STARTS A NEW TURN [5, p. 86].
5. "All my book represents a passionate sermon of the holistic approach… It is difficult to oppose holism (wholeness) as a basis of scientific ideology; its authority is evident, its truth raises no doubts – ultimately, space is integrated and interrelated, any society is integrated and interrelated, any human is integrated and interrelated, etc. But the holistic approach nearly never finds an application in science; it is still not utilized as it should be, namely as a method of world perception. Lately I have been getting more inclined that atomistic way of thinking[12] should be regarded as a mild form of psychopathology, or at least a component of cognitive immaturity syndrome" [5, pp. 13-14].
Tremendous!!!
6. "When we are talking about prepotentiality hierarchy one may gain an impression that the matter concerns a needs structure that is rigidly fixed.
7. I am afraid that our discussions may urge reader's thought in a wrong direction.
8. It may SEEM that the hierarchy of 5 groups of needs we have described denotes specific dependence – a need once satisfied is easily replaced with another. Hence a possible wrong conclusion: a need may only arise after a lower level need has been satisfied a hundred percent. Actually, it may be said about nearly every healthy member of our society that he is satisfied and unsatisfied at the same time in all of his basic needs. None of the above mentioned needs ever becomes the only, all-absorbing motive of human behavior... practically every behavioral act is determined by multiple determinants or multiple motives" [5, p. 101] (marked in bold type by the writers).
Hence four conclusions: (1) The "needs pyramid" is same thing as the notorious "25-th TV frame" or psychological subversive activity against humanity unleashed by scientists incapable of holistic thinking; (2) A. Maslow's warnings against simplification of his a hundred percent holistic theory were realized exactly vice versa; (3) Abraham Harold Maslow never plotted any pyramid (unlike Russian bankers) and never expected others to do it for him; (4) it was only about a spiral. And it could not be other way.
To investigate what the geometrical figure of "spiral" is associated with and reflected in mass consciousness, a brief philological research using "Internet polling" was carried out. The outcome was as follows:
Supposing the considerations we have brought against the pyramid and for the spiral are sufficient, we[13] suggest to correct the tragic mistake of mankind's mentality and plot Maslow's cylindrical spiral of basic needs. That would be the best gratitude to the genius psychologist and doctor, a holistic scientist who gave the humanity a practical aid for developing one's personality and life strategy, and, respectively, for guiding one's fate.
Before plotting the geometrical "shrunk figure" of basic needs, let us turn to today's problems. Abraham Maslow has not lived only one year to the "Earth's Day" and therefore he could not hear such phrases as "global ecological crisis", "global deterioration of health", and he could not know about ecological problems of mankind which not only generated this notion but are posing a threat to the very existence of human population - "homo sapiens". The mankind held up three[14] world summits. By the way, that was the only reason for 178 governments to get together. In 1992 the "Agenda for XXI Century" was adopted - a multinational program for getting out of global ecological crisis, or a strategy of sustainable development. In 2002 at "Rio + 10" summit it became obvious that this program generated by thousands of scientists and consisting of 104 documents has failed. It gives cause for mankind to go into hysteric. The analysis shows that those 178 heads of governments are not intellectually hopeless, but there are forces that could not be overcome by investing any amount of money or by employing the best contemporary minds: (1) it is total differentiation of knowledge that made the Earth's population silly by the XXI century [1, pp. 94, 48, 19 and many others] with the current system of education breaking ties in people's minds and propagating the "atomistic way of thinking", according to Maslow (see paragraph 6 above). (2) it is inertia of human consciousness (let us recall an example from human history when it took from 100 to 300 years for humanity to switch from geocentric to heliocentric system of the Universe. (3) it is motivation of human actions (the Maslow theory is all about!): the number of anti-ecological actions[15] is 6 billion people with anthropocentric consciousness multiplied by (24 less 9 hours for sleep) hours = 32 850 000 000 000 = nearly 33 trillion actions a year[16] , which means that "our yearly reality consists of dozens of trillions of anti-ecological human actions. A human action is determined by the following categories: basic and other needs, motivations, intentions, goals, emotions, consciousness, will, way of thinking, attitude to the opinion of others, personality trends, and upbringing conditions. A motive is the "crucial" element of a human action and determines the pattern of behavior. An action can be motivated by a duty (e.g. those prescribed [ See 1, pp. 82-90]:
noospheric norms of huaman behavior
Recognize values common to all mankind such as life, ecological well-being and human health as priority values.
Recognize the necessity of changing the anthropocentric thinking of the major part of humanity to ecologocentric one to preserve human population in biosphere.
Guide ourselves in our actions by double-sided status of man in biosphere: a human is not only a consumer of nature but an integral part of it totally depending on the environment.
Realize that humanity's only chance to survive is to resolve ecological problems by joint efforts of people of all nations and confessions.
Take it as a guide to action that the ecological crisis has put forward principally new ecological and social challenges faced by humanity which require a qualitatively new (integrative) level of education for the whole mankind.
Recognize that loss of the instinct of self-preservation by mankind is a result of global delimitation of sciences into sciences of the living and sciences of the lifeless.
Reconstruct the system of education and upbringing of the Earth's population based upon two desmoecological principles: everything is interrelated, "the living and the lifeless are Siamese twins" the separation of which is lethal for the both.
Translate the philosophy of survival into concrete deeds – not to allow uncontrolled growth of human population and ecological offences, and to monitor the environment.
Develop only "ecologically compatible", resource-saving technologies, subject them to ecological expertise based on the principle that nature is exhaustible, and there is no such notion as "rubbish" in nature.
Ecological imperatives are inevitable and must be laid in the foundation of everyone's life strategy, as well as of the national, regional, and world policies. Denial of this requirement is posing a threat of environmental degeneration
Norms of human's behavior may be referred to dominant laws – this is a strategy of all other strategies. Dominance of laws is determined by a dominant block of fundamental laws of a system that defines the nature and structure of other laws. Dominant laws define the major attribute of the global system. This attribute is life for organic nature, anti-entropic processes for a geographic shell, and consciousness for a society [1, pp. 92-93] – these are deep-root consequences and a field of activity for Maslow's holistic theory. (4) And, at last, these are not the "right"[17] values common to all mankind. Something should be done about it.
Thus
a hundred percent holistic "Desmoecology – educational theory for
sustainable development" appeared in 1997-2003. A
shrunk form of desmoecology based on 7 axioms[18]
is described by 7 following descriptors from its thesaurus[19]:
(1) The global ecological crisis. (2) Universal values and noospheric norms of
human behavior. (3) Biotic regulation of the environment. (4) Self-organization
(chaos, bifurcation, order). (5) Ecological and social responsibilities. (6)
Differentiation and Integration of knowledge and human society. (7) Professional
competence of broad specialists and higher institution teachers: candidates of
science, doctors of science, senior lecturers, and professors [1, p. 30].
The problem of the first health level – the physical health is also unsolvable.
This is the most obvious problem: physicians and psychologists have come to a common opinion that in practice there are no physically healthy people but relatively healthy ones who do not apply to a doctor.
That is why the task of recovering one's physical health comes up.
But here exists the same problem that was discussed for the two above levels (social and psychological) - "total differentiation of knowledge and reality" or an "atomistic way of thinking", respectively.
What does it mean in practice? Professor I.P. Chepurnoy[20], author of 8 postulates referring to the function of human genome wrote, "The human organism is still considered to be consisting of different organs functioning by themselves. There is no unified concept of human organism functioning as a single whole, to say nothing of a system controlling all these organs as an integral system. Doctors divided human organism into components, they created specialization depending on function of this or that organ, and they try to gain understanding of an organ in isolation from the whole organism…For example, a dentist only knows the structure and function of teeth. One may think that our teeth exist separately from the whole organism and they sit separately on a shelf. That is why a dentist does not know which components contained in blood form the teeth tissue, or what abnormalities in blood composition may lead to broken synthesis of teeth enamel glycoproteids, dentine, and cement. Accordingly, he cannot understand a cause of dental diseases (e.g. caries, dental abscess), and what is most important, he does not know how to eliminate a disease so that a human would not have the same problem in future, apart from filling a tooth hole or pulling a tooth out and replacing it with an artificial one. But dental tissue cells carry certain information for the whole human organism – e.g. food temperature and acidity level. Naturally, an artificial tooth transmits no information to the organism. Human's organism maintains the teeth function by constantly replacing dead cells with new ones. The dead cells are decomposed into smaller complex compounds and taken out through blood vessels or exteriorized in a form of dental calculus – we remove such dead cells when brushing our teeth". Another example. "Now cardiologists stick to only one operation - coronary bypass surgery. At present it is prestigious and fashionable to perform the bypass surgery in rich people, though in principle all this operation is based on a very primitive approach. If your cardiovascular system gets clogged with lipoproteins of low density (complex compound of proteins and adipose tissue) due to excessive consumption of proteins and lipids then an artificial vessel is added to a restricted one. A plumber does the same when a water pipeline gets clogged: he installs a temporary bypass pipe. However later on he tries to remove or clean up the clogged area…But cardiologists do not remove such a bypass and, what is more important, they do not eliminate the cause of blood vessel clogging, and a patient goes on clogging his or her own blood vessels with lipoproteins of low density. This problem can be resolved easily. One should simply decrease consumption of proteins and lipids: formation of plaques will stop, and a blood vessel will not be further clogged. When recovering, the organism itself will remove the plaques it had formed before" [8 , pp.19-20].
"Not knowing interrelationships among different human organs, doctors try to substitute a diseased organ for a healthy one (donor organ). But this does not bring a "lasting" health to a person because biochemical disturbances taking place in human's organism contribute to developing a disease in this or that organ. Thus transplantation of a healthy organ to a patient with biochemical disturbances, the reason of which had not been eliminated, will lead to a recurrent disease in that organ over a certain period of time. Therefore, the optimum process that can guarantee a healthy life to a patient for a long time is restoring cells of a human organ" [8 , p. 22].
In practice, the doctors' "atomistic way of thinking" does not mean health recovery but a temporary health improvement, and wasting money on deadlock research of separate organs' functions. That is why a hundred percent holistic theory was developed by Professor I.P. Chepurnoy (from Sravropol city of Russia) based on writings of I. P. Pavlov, a Nobel Prize winner, and other professors – V.A. Shaternikov, G.I. Bondarev, A. M. Ugolev, among others, and based on 7[21] integrative postulates. This theory is not aimed at restoring the function of a separate organ, but at recovering processes taking place in the whole organism, in all its seven systems (digestive, respiratory, vascular, musculoskeletal, immune, reproductive, and nervous-and-brain systems), and therefore is aimed at restoring the whole organism. The circle has closed. Life demands unification of three "holistic", "integrative" theories into one metatheory:
1. Educational theory for sustainable development, behavior theory of a human and mankind as a whole on a social level (A. Boussygin).
Human motivation theory, i.e. theory of personal behavior on a psychological level (A. Maslow). Health recovery[22] theories, i.e. discussion of metabolic processes in all seven systems of the whole human organism on a biochemical level (I. Chepurnoy).
That was historically logical, starting with V. Bekhterev's idea he presented at the beginning of the XX century[23]. We are not just implementing a legacy of the genius "holist": these theories call for unification. This is unification through an integrative, bio-psycho-social category which is most important for any human – the category of health (healthy life-style), a need that became BASIC by the beginning of the XXI century.
Plotting a spiral is not a difficult task if we recall that a spiral (spiral of life and needs) according to A. Maslow is infinite, but at different moments of life it is individual (Fig. 1).
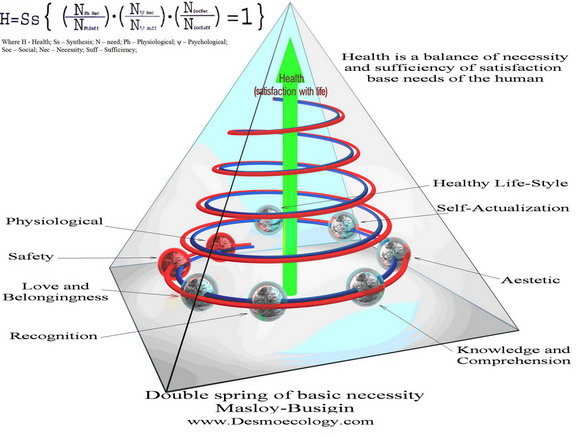
Fig. 1 Maslow-Boussygin's spiral of basic needs
Horizontal section of the cylindrical spiral of needs (picture of a life's moment) is a circle. The best achievement of the world thinking (Fig. 2) in the sphere of management (universal idea developed within International standards - ISO 9000 series, 2000 version ) is also a circle - "quality management circle" (quality of product, technological process, education, and, why not quality of health or life?). Every time recalling this achievement one has to draw a trivial, "holistic" conclusion and, following B. Commoner, admit that "all is interconnected with everything" and "all are interconnected with everybody"[24], and the world is integrated. These are not only theoretical conclusions by holistic scientists but it is what is happening in real life (See "Health Chart for a Healthy Person").
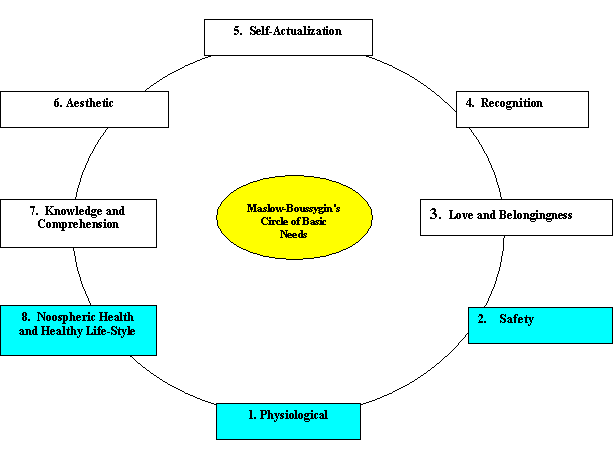
Fig. 2. Maslow-Boussygin's circle of basic needs
Now the last task we have set for ourselves in this article (see [1,2 – «genius' formula) »] for further details) is to give a "shrunk", mathematized definition of the health notion. To analyze the health notion, we have used a systematic approach[25].
To formulate the health definition, we have applied synthesis[26] as a process of system formation.
Let
us remind you that main systems principle is that of integrity (system
properties cannot be reduced to a sum of properties of its components, and vice
versa, system properties cannot be drawn from a sum of properties of its
components)[27].
Therefore we have always been interested to know what is that elusive component that is "above"
a sum[28]
of components. What is particular about it and what
adds a new quality to a system as compared to a sum of properties? The
answer will be apparently different in each single case but in this very case we
set up a hypothesis that it is a question of synergism[29]
of interrelationships among three needs (health). We can bring about a
well-known and easily understood example of physiological capabilities
multiplied in a critical situation under the influence of fear (e.g. when
running from an angry dog), or in anticipation of a high award, etc.
When
generating the health notion number 1, we arrived at the conclusion that health
is a dialectical triune entity and, simultaneously, a means, a process, and a result of necessity and sufficiency balanced
in equal satisfaction of physiological, psychological, and social needs of man.
The
hypothesis of synergism (multiplication) of interrelationships among all three
needs enables us to put a multiplication sign (•)
between basic needs, to equal the equilibrium of necessity and
sufficiency to 1, to designate the
health notion with { } and "processability"
of health category with sign of synthesis. Unfortunately,
neither mathematical handbooks nor doctors of physics and mathematics we apply
to, nor Internet sources could help us in finding appropriate symbolism. It
turns out that a mathematical symbol for expressing the process of synthesis
does not exist in science. Therefore we have decided to fill up the gap by
assigning "Ss" symbol to the "synthesis" notion.
As a result we have a simple[30],
qualitatively and quantitatively mathematized description of SYSTEMS
SYNTHESIS, or what is probably more correct, the ascending "synthesis
of systems approaches": (1) systems approach to
human organism as a biochemical system (I. Chepurnoy, physiological level); (2)
systems (holistic) approach to human's mentality on all levels of higher needs,
not only basic ones (A. Maslow); (3) systems (desmoecological) approach to
activities of a human and mankind (A. Boussygin, social level).
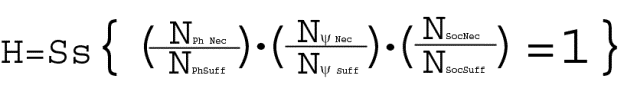
where:
H – health;
Ss - synthesis;
n-
needs: Ph –
physiological, Y
- psychological, Soc - social;
Nec
–necessity; Suff
- sufficiency[31].
It means we have got a formula of a wise, healthy, satisfied with "smooth" life human – the golden mean which may not be absolute happiness (which according to Maslow cannot be permanent) but at any rate is not misery.
Design-mathematical benefits of this notation are insignificant but the
methodological, gnoseological, and goal-oriented benefits are undoubtful. They
can be utilized as a compass, a means of orientation, planning of life strategy,
or as an object for criticism. To criticize the logical and large in size
Chepurnoy-Maslow-Boussygins' treatises by each thesis is not to everybody's
competence and liking. A shrunk to one line and therefore easy to read notation
of synthesis of three holistic theories can be perfectly criticized. Therefore,
we would be very grateful to those who would not only present critical arguments
but offer his or her own options of holistic
solution to
resolving health problems[32]
of healthy people.
Recognizing the complexity and insufficient study of this theory in special
literature, we realize that the "THEORY OF HEALTH
OF A HEALTHY PERSON"
we have presented here is only a tiny top of an iceberg.
The third Cheeseholm law reads, "any proposal is interpreted by people differently as it was meant by those who offer it". To conclude this article with A. Blokh's witty statement, we would like to add that both consequences of this law (ECO journal, No. 1, 1983) call for a discussion that might help more talented people reveal moments of truth not only in what has been stated above but what is hidden deep beneath the surface of the problem and what we have failed to see.
Our address:
P.O. Box 4601, 443080 Samara, Russia, or email: busigin @mail.radiant.ru
[1]
Term yet little known to scientific community and relating to philosophy of
education. Desmoecology is a
science coordinating other sciences, or is an integrative socio-pedagogical
field of knowledge dealing with interrelationships among natural, economic, and social
aspects of the ecological problem. The task of desmoecology is to form
conceptually and socially balanced mentality in an ecologically minded
person. The term of desmoecology appeared in 1996; derived from "desm"
(Greek) which means "connection"
[2] holistic in Maslow's terms
[3] after Sigmund Freid
[4]
because it is never known beforehand, which needs of an individual, if not
satisfied, will have the worst effect on his or her organism
[5]
noosphere is understood
in desmoecology as a result of organized vital activities of society
characterized by priority of health, ecological wellbeing, and Life on Earth
based on integrative Mentality, sense of Duty of humans towards each other
and towards Nature
[6] to help a student organize this activity and identify his or her bio-psycho-social state at lectures and practical training on psychology and ecology, we have developed a special "Health Chart for a Healthy Person"
[7]
noospheric health model is integrative per se, but (in our opinion) the term
is "taken up" with nonsense
[8] proved by checking dozens of textbooks on psychology and management. Judging by reader's record cards we have checked, none of thousands of university students has ever borrowed this book from a library in 5 years! Same unfortunate thing happened to another author - American scientist, ecologist Barry Commoner. His book ("The Closing Circle", New York, 1971) was published practically at the same time as Maslow's "Motivation and Personality" but it has never been borrowed from a library by a student in 25 years! Barry's "followers" bring about only four of his remarkable aphorisms quoted in all textbooks on psychology, passing them for laws of "social ecology". But the principal Commoner's achievement – analysis of the "new after-war industrial technology" - technology that accounted for a leap in global ecological crisis and mass impoverishment was never noticed! [1, p. 51]
[9] at Rio summit in 1992 heads of 178 governments (considered to be the most clever people) failed to draw an effective plan of getting mankind out of the global ecological crisis
[10] as for the origin of the pyramid, we can offer a hypothesis that the pyramid ascribed to Maslow was evoked by dollar-imperial state of mind of American interpreters of the outstanding psychologist who never meant anything of the kind (the pyramid on a US one dollar bank note symbolizes force and strength. The motto under the pyramid - "NOVUS ORDO SECLORUM" or "New Time Order" means "Beginning of a New American Era"
[11] that is why A . Maslow's writing is not read in the original
[12] "total differentiation" of desmoecological terms
[13] two doctors of pedagogical sciences, professors, heads of chair of "ecology and ecological education" and "psychology", respectively
[14]
in Stockholm in 1972, in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, and in Johannesburg in 2002
[15] if done approximately one per hour (though more often in private life)
[16]
does humanity have enough money to compensate for this crazy number of
ecologically ignorant actions?! And
will never have
[17] technocratic [1, p.62]. Technosphere is understood in desmoecology as a result of organization and management of vital activities of people, characterized by priority of satisfaction of their material needs and power ambitions based on total differentiation of knowledge and total technicalization of biosphere
[18] derived from axiology (theory of values) and ecology; underlying, running through the whole department of this knowledge, and coordinating other fields
[19]
"thesaurus" translated from Greek means «code of notions»,
"thesa" means a notion; "aura" means a code, a shell.
Primary methodical units in a thesaurus of knowledge domain are
descriptors. Descriptor is a key word reflecting its main contents. A key
word is a notional dominant
[20] under his theory (and according to his words), B. Yeltzin, M. Gorbachov, and V. Chernomyrdin recovered their physical health [8, стр.6]
[21] the number of «7» was not agreed with Professor Chepurnov because, unfortunately, we never met him personally
[22] spoiled by ecological and universal crises
[23] about one hundred years spent on development of a seemingly simple idea seems to be too much time. V.M.Bekhterev articulated his concepts in his report "Personality and Conditions for Development and Health" at the second congress of Russian psychologists in Kiev in September of 1905; those were fundamental for further development of health psychology
[24] one of 7 desmoecological axioms [1, p.117]
[25]
System (from Greek "systema" – a whole comprised by parts;
a combination), set of interrelated elements forming integrity, unity
[26]
Synthesis (from Greek
"synthesis" — joining, composition), combination of separate
elements or parts of an object into a whole (system)
[27]
I. Kant developed principles of systems nature of knowledge in classical
German philosophy: according to his theory, scientific knowledge is a system
in which a whole dominates over components
[28]
Naïve, non-holistic attempts of people with "atomistic
thinking" to derive a formula
of health were as follows:
[29] corporate action, multiplication
[30]
«easily seen»
[31] B. Yeltzin who gave over the reins of power to V. Putin in due time proved to be an example of wise attitude towards one's own health and life
[32] as well as knowledge, noospheric morality, intellectual development (conceptual and social) [1, pp. 54,82,144 and other], [2, ch. 2]
References:
1.
Бусыгин А.Г. Десмоэкология
или теория образования для
устойчивого развития. Книга первая.
Симбирск: Изд-во «Симбирская книга», 2003.-224
с., ил. (Boussygin, A. G. (2003) "Desmoecology
or Educational Theory for Sustainable Development", Book 1. Simbirsk:
"Simbirskaya Kniga", 224 pp., ill.)
2.
Бусыгина А.Л. Профессор
–
профессия: теория проектирования содержания
образования преподавателя вуза. Самара:
Изд-во СамГПУ, 2003, издание 2-ое, испр. и доп.
- 197 с., ил. (Boussygina, A. L. (2003) "Professor
– Profession: Theory of Designing the Content of Teacher's
Education at Higher Institutions". Samara: "SamGPU", 2-nd
Edition, Rev. & Suppl., 197 pp., ill.)
3.
Государственный
доклад о состоянии здоровья
населения Российской Федерации в 2002 году.
М.: ГЭОТАР-МЕД,
2003. - 100 с.
("State
Report on the Russian Population's Health
in 2002" (2003). Moscow: "GEOTAR-MED", 100 pp.)
4.
Калью П.И. Сущностная
характеристика понятия «здоровье» и
некоторые вопросы перестройки
здравоохранения: обзорная информация. - М.,
1988. – 220 с. Kalyou,
P. I. (1988) "Essential Characteristic of Health Notion and Some Issues of
Restructuring the National Health Care", Review. Moscow,
220 pp.)
5.
Маслоу Абрахам
Г. Мотивация
и личность. Перевод с англ.
Татлыбаевой А. М.— СПб.: Евразия, 1999.— 479
с. (Maslow,
A. "Motivation
and Personality". Translated from English by A. Tatlybaeva
(1999). Moscow: "Evrasia", 479 pp.)
6.
Овчаров Е.А.
Социальная
и экологическая
обусловленность
здоровья
населения: Учеб. пособие
- Нижневартовск:
Изд-во
Нижневарт.
пед. ин-та,
1993.-100 с.
(Ovcharov, E. A. (1993) "Social
and Ecological Conditionality of People's Health".
Nizhnevartovsk: "Nizhnevartovsk Pedagogical Institute,
Publishers", 100 pp.)
7.
Психология
здоровья:
Учебник для вузов / Под ред. Г. С.
Никифорова. — СПб.: Питер, 2003. — 607 с.: ил.
— (Серия «Учебник для вузов»).
(Nikiforov, G. S., ed. (2003) "Psychology
of Health", Series: Textbook for Higher Institutions. St. Petersburg:
"Peter", 607 pp., ill.)
8.
Чепурной И.П. Питание
и здоровье человека.
- М.:Издательско-торговая корпорация «Дашков
и К0»,2003.-208 с. (Chepurnoy,
I. P.
(2003) "Food
and
Human
Health". Moscow: "Dashkov &
Co.", 208 pp.)
9.
Byer Curtis 0., Shainberg Louis W. (Mt. San
Antonio College). Health in Your
Hands. (Байер К.,
Шейнберг Л. Здоровый
образ жизни: Пер. с англ. — М.: Мир, 1997.—368
с., ил.)